Power-to-gas is the name given to an energy process and storage technology which allows electricity to be held in reserve in the megawatt range. Existing network infrastructure can be utilized by linking existing power and natural gas grids. This allows seasonally adjusted storage of significant amounts of power and the provision of CO2-neutral fuels in the form of the resulting renewable energy source gas.
Power-to-gas represents a complete system solution to the problem of surplus energy reserves on the way to a new renewable energy age.
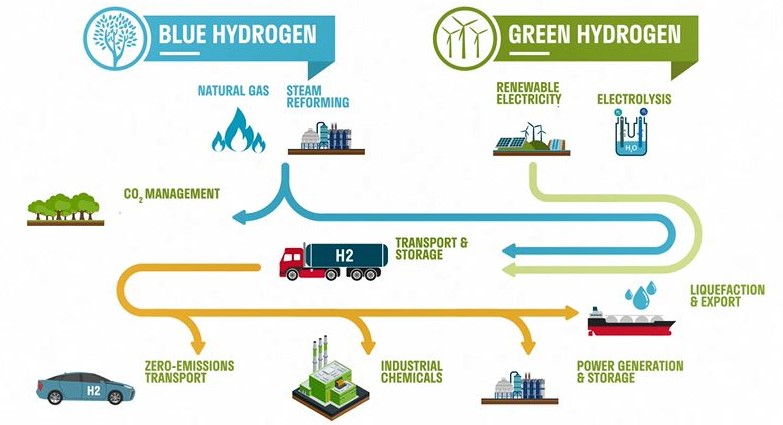
The Korean Renewable Energy 2030 Implementation Plan expects an increase in renewable energy installation capacity but highlights the need for technology to store excess electricity and stabilize power supply. Power-to-Gas, which converts electricity into hydrogen and methane, can effectively store excess electricity.
Now, Korea’s policy for developing and promoting large-capacity energy storage technology has mainly focused on lithium-ion batteries. As a result, research on hydrogen storage in connection with renewable energy, such as Power-to-Gas (P2G), is still in its early stages. Domestic companies specializing in water electrolysis mainly rely on foreign technologies.
To support the development of renewable energy and water electrolysis, the Korean government has been funding empirical research projects since the end of 2015. However, the lack of domestic companies with original P2G-related technologies has made them dependent on foreign technologies.
Recently, the city of Changwon, with support from the central government, invested a total of KRW 93 billion to build a hydrogen filling station (phase 1) and a hydrogen production facility using compressed natural gas (CNG) (phase 2). The construction of a reprocessing device (step 3), a hydrogen liquefaction device, and a storage device (step 4) was also completed. Additionally, a hydrogen-electric fusion energy demonstration complex, linked to solar power and fuel cells, was built.
Further, The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy announce the designation for the hydrogen-specialized complex in the second half of 2023. An official from the Ministry of Industry announced that it plans to continue supporting and nurturing the hydrogen-specialized complex so that it can play a key role in the development of the hydrogen industry.
Despite these efforts, there is still a long way to go in the development of P2G related technologies in Korea.
As part of efforts to reduce carbon dioxide, the main culprit of greenhouse gases, the P2G industry is just in its infancy in Korea, but the Korean government’s will to develop P2G as a national institutional industry is getting stronger.
Anyhow, Blue hydrogen production facility projects are underway in Korea. National Korea Gas Corporation has decided to import green hydrogen from abroad from 2025.
South Korea is still focusing on blue hydrogen production because there is still a lack of infrastructure that can produce green hydrogen, such as offshore wind power generation.
I don’t know the future of human beings, but I think we have to go in the direction of getting better and better.


